By Richard Frost, Head of Consulting, Armata Cyber Security
The traditional notion of establishing a secure perimeter around organisational networks is outdated today, thanks to the mainstream establishment of remote work and cloud-based services. In addition, the emergence of advanced persistent threats (APTs) has rendered the concept of a trusted internal network perimeter ineffective.
Armata Cyber Security proudly offers Zero Trust security to harden your organisation’s security posture as another example of how we facilitate the newest security technologies for today’s working environment. The Zero Trust model represents a fairly recent paradigm shift in cyber security.
An Enormous US Data Breach Spurs on Zero Trust Uptake
In 2015, the US government saw one of the largest breaches of its data in history when the Office of Personnel Management (OPM) suffered a data breach involving the exposure of an estimated 22.1 million records. The information revealed included Social Security numbers, names, dates and places of birth.

Image courtesy of ABC News
This data breach caused the American government to launch several initiatives to improve and modernise its security posture, and the Zero Trust approach, already in existence, began to be explored in a more mainstream manner as a result of some of the activities launched in the wake of this breach.
In August 2020, the American National Cybersecurity Center of Excellence (NCCoE) arm of the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) released the general guidance document NIST SP 800-207, ‘Zero Trust Architecture’, for use within the federal government. This document provides conceptual-level insight for zero trust and zero trust architectures, including deployment models, use case scenarios and discovered gaps in technologies.
It can thus be seen that Zero Trust architecture is endorsed at the highest level of US national cyber security protection.
‘Never Trust, Always Verify’

This phrase lies at the heart of the Zero Trust cyber security approach. Instead of operating on a default assumption that entities within a network can be inherently trusted, the Zero Trust approach instead acknowledges that threats can emanate from both external and internal sources, requiring a more adaptive and dynamic security model.
Zero trust security architecture is built to reduce a network’s attack surface, prevent lateral movement of threats, and lower the risk of a data breach. Such a model puts aside the traditional ‘network perimeter’ – whereby all devices and users are trusted and given broad permissions – and replaces it with least-privileged access controls and multi-factor authentication (MFA). In addition, the assumption is made that a security breach is a matter of ‘when, not if’.
‘Assume Breach’
One of the key drivers of the Zero Trust cyber security approach is the prevalence of advanced persistent threats. These sophisticated, long-term cyber attacks often circumvent traditional security measures by exploiting vulnerabilities or employing deceptive tactics.
Zero Trust mitigates the risk of APTs by continually verifying the identity and trustworthiness of users and devices, making it challenging for attackers to move laterally within a network undetected. Within this context, following a Zero Trust approach means that the IT security team follows an ‘Assume breach’ position.
Against this background, the Zero Trust security framework has gained significant importance, because approaching planning from an assumed breach perspective allows an organisation to be proactive rather than reactive with its security posture, as it improves processes and solves scaled problems.
Armata Partners with Appgate SDP
A mature Zero Trust security programme is proven to harden enterprise defences, but it must also reduce complexity, accelerate secure digital transformation, and improve operational efficiency.
Armata has chosen to partner with one of the industry’s most comprehensive Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) solutions, Appgate SDP.
In a world where trust cannot be assumed, Appgate ensures that every user and device is treated as untrusted until proven otherwise. This approach mitigates the risk of unauthorised access and lateral movement within networks, a crucial defence against today’s advanced cyber threats.
Armata offers Appgate SDP deployment with a unique as-a-service approach that retains customer control of network traffic, and reduces infrastructure management overheads. The platform’s featured risk engine service enhances access policies with rich security context via click-to-configure connections to third-party IT, security and business solutions.
Robust features and benefits of Appgate Zero Trust solutions include the following:
- Ingested risk telemetry from network, IT, security and business systems;
- The enablement of no code, click-to-configure integrations;
- The delivery of innovative risk engine technology;
- Allowing customisable risk rules to dynamically drive policy;
- Significantly smaller attack surfaces; and
- Offering customers the choice of deployment and hosting models.
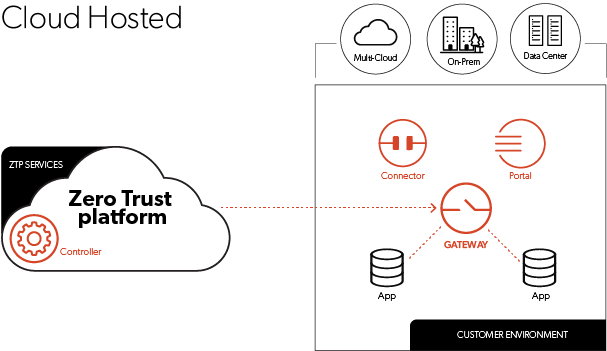
Image courtesy of Appgate SDP
In addition, Appgate’s contribution to Zero Trust includes the implementation of Micro-Segmentation, which is a strategy that enhances security by dividing the network into smaller, isolated segments. This means that even in the event of a breach, the lateral movement of threats is restricted, minimising the potential impact.
With the rise of remote work, securing access to corporate resources from anywhere is critical. Appgate’s solutions enable secure access regardless of location, enabling the workforce to remain productive without compromising on security.
